If you’ve ever used an Instagram filter, played Pokémon GO, or seen a demo of the Apple Vision Pro, you’ve already stepped into the world of extended reality. But with a sea of confusing acronyms like AR, VR, and MR, what’s the actual difference? Let’s break it down with simple, everyday examples.
This 5-minute guide will give you a clear understanding of each technology, what it’s used for, and which one is right for you.
The Ultimate AR vs. VR vs. MR Comparison Chart
| Feature | Augmented Reality (AR) | Mixed Reality (MR) | Virtual Reality (VR) | Extended Reality (XR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Immersion Level | Low (Digital Overlay) | Medium (Interactive Overlay) | High (Fully Digital) | All levels (umbrella) |
| Real World View | Visible | Visible & Interactive | Blocked Out | Varies (AR, MR, VR) |
| Key Hardware | Smartphone, Smart Glasses | Advanced MR Headsets | VR Headsets | XR Headsets (support AR/VR/MR) |
| Popular Example | Pokémon GO | Apple Vision Pro | Beat Saber | Meta Quest Pro, Apple Vision Pro (XR mode) |
| Cost Range | $0 - $300 | $500 - $3,500+ | $300 - $1,000+ | $300 - $3,500+ |
| Best For | Information overlay, social media | Productivity, spatial computing | Gaming, training, therapy | All immersive experiences |
The Simple Breakdown: Understanding the Virtuality Continuum
Think of immersive technologies as a spectrum called the Virtuality Continuum - from the completely real to the completely virtual. It’s like a slider for immersion. On one end, you have the physical world. On the other, a fully digital one. All these technologies live somewhere on that slider.
Augmented Reality (AR): Enhancing Your World
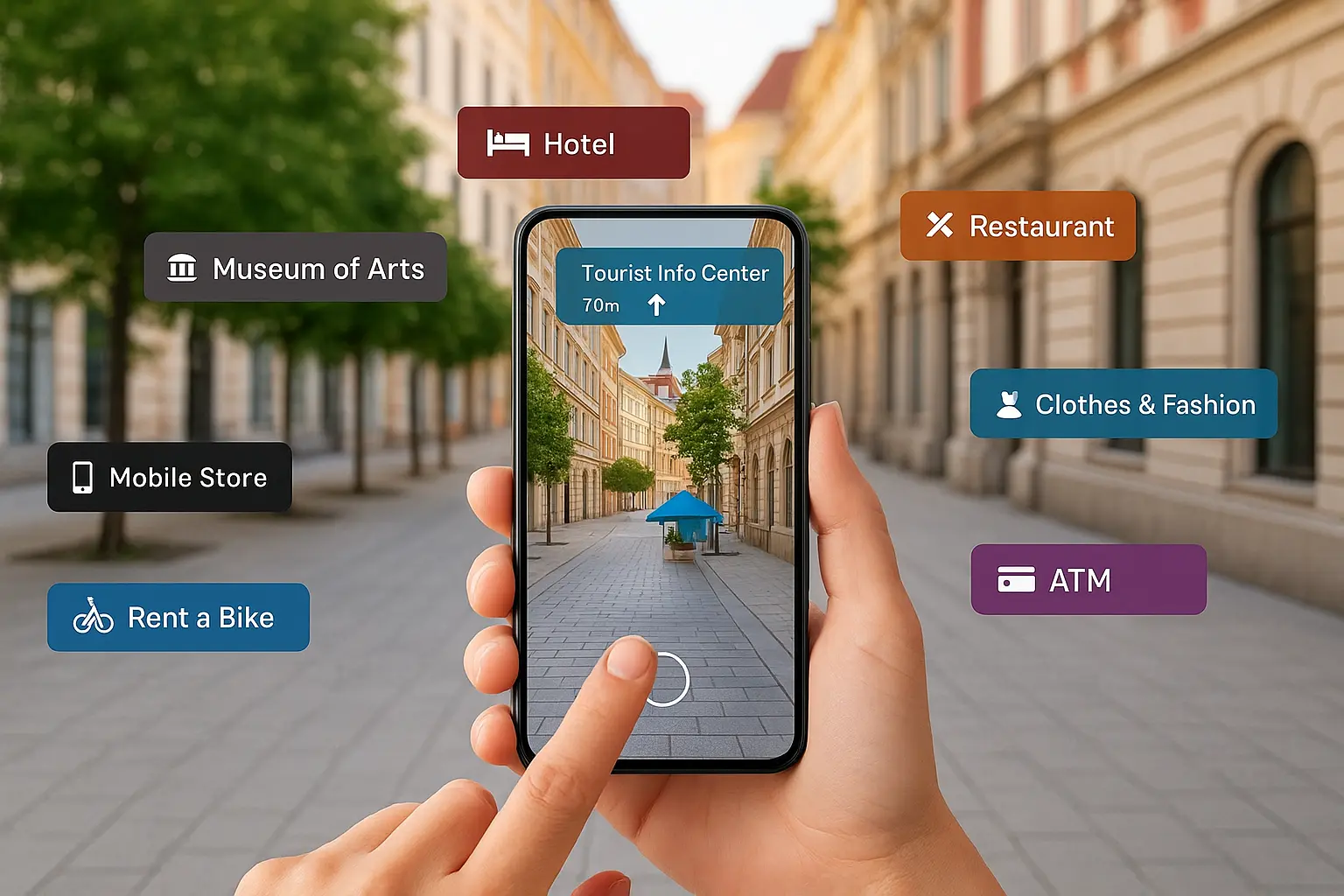
AR overlays digital information onto your view of the real world. It augments your current reality without changing it.
Real-World Example 1: Pokémon GO
The most accessible AR experience. Digital characters appear in your real-world environment viewed through your phone. You walk around your neighborhood, but now Pikachu sits on your actual sidewalk. For more on how AR is changing entertainment, see How AI is Used in Video Games.
Real-World Example 2: IKEA Place App
See how furniture looks in your actual room before buying. Point your phone at an empty corner, and a virtual couch appears - sized and positioned exactly as it would be in real life. Curious about AR in retail? Check out AI Tools for Retail.
Real-World Example 3: Snapchat Filters
Transform your face with digital effects in real-time. Add bunny ears, change your eye color, or place yourself in a virtual world - all while seeing your actual surroundings.
Key Hardware: Smartphones, tablets, and smart glasses like the Ray-Ban Meta glasses. Learn about AI-powered meeting tools that use similar technology.
Cost Range: $0 (smartphone) to $300+ (smart glasses)
Virtual Reality (VR): Replacing Your World
VR completely blocks out the physical world and immerses you in a fully digital environment, tricking your senses into believing you are somewhere else.
Real-World Example 4: Beat Saber on Meta Quest 3
You’re standing in your living room, but your brain thinks you’re in a neon-lit tunnel slicing through blocks with lightsabers. Your physical surroundings disappear completely.
Real-World Example 5: Surgical Training Simulations
Medical students practice complex procedures in a safe, repeatable virtual space. They can make mistakes without consequences while developing muscle memory for real operations.
Real-World Example 6: VR Therapy for Phobias
Patients with fear of heights can gradually expose themselves to virtual heights in a controlled, safe environment. The brain responds as if it’s real, but there’s no actual danger.
Key Hardware: VR headsets like Meta Quest 3, PlayStation VR2, and Valve Index.
Cost Range: $300 (Meta Quest 3) to $1,000+ (high-end PC VR)
Mixed Reality (MR): Interacting with Both Worlds

MR is advanced AR. It not only overlays digital objects but makes them aware of your physical environment, allowing real and virtual objects to interact.
Real-World Example 7: Apple Vision Pro
When you see a virtual browser window floating in your living room and a virtual ball bounces off your real coffee table, that’s MR. The digital objects understand your physical space. See how spatial computing is changing work.
Real-World Example 8: Meta Quest 3’s First Encounters
Digital aliens break through your actual walls and ceiling. The game knows where your furniture is and uses it as cover or obstacles. Explore more about immersive gaming.
Real-World Example 9: Microsoft HoloLens in Manufacturing
Workers see holographic instructions overlaid on real machinery. They can interact with virtual buttons and see real-time data while keeping their hands free for actual work.
Key Hardware: Advanced mixed reality headsets like Apple Vision Pro, Microsoft HoloLens 2, and Meta Quest Pro. Discover how AI video tools enhance MR experiences.
Cost Range: $500 (Meta Quest Pro) to $3,500+ (Apple Vision Pro)
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
Extended Reality (XR): The Umbrella Term
XR stands for Extended Reality—the umbrella term for all immersive technologies that blend the real and digital worlds. XR includes:
- Augmented Reality (AR): Digital overlays on the real world
- Virtual Reality (VR): Fully digital environments
- Mixed Reality (MR): Digital and real objects interacting together
The tech industry uses “XR” to describe hardware, software, and experiences that combine any or all of these technologies. For example, XR headsets can support both VR and MR modes, and XR developers build apps for the entire spectrum.
Industry Applications: Where Each Technology Shines
Augmented Reality (AR)
- Healthcare: Overlay patient data during surgery, AR glasses for vital signs
- Retail: Virtual try-on, in-store navigation
- Education: Interactive textbooks, 3D models
Virtual Reality (VR)
- Gaming: Immersive experiences, VR arcades
- Training: Flight simulators, safety drills
- Therapy: Exposure therapy, stress reduction
Mixed Reality (MR)
- Manufacturing: Holographic assembly, remote expert help
- Architecture: Virtual walkthroughs, collaborative design
- Remote Work: Virtual offices, spatial whiteboards
Extended Reality (XR)
- All Sectors: Unified platforms, cross-technology apps
- XR Headsets: Support AR, VR, and MR modes
- XR Developers: Build for the full spectrum
How to Choose the Right Technology for Your Needs
Choose AR if you want to:
- Add info to your real world
- Use your phone or glasses
- Stay aware of surroundings
- Start with minimal investment
Choose VR if you want to:
- Escape into another world
- Focus without distractions
- Train in safe, repeatable environments
- Experience full immersion
Choose MR if you want to:
- Blend digital and real objects
- Work with spatial computing
- Have the most advanced experience
Choose XR if you want to:
- Develop or use apps across AR, VR, and MR
- Future-proof your investment
- Access the full spectrum of immersive tech
The Future of XR: What’s Next in 2025 and Beyond?
The lines between these technologies continue to blur. Here’s what’s coming:
- Smaller, lighter AR glasses that look like regular eyewear (Statista: AR hardware trends source)
- Advanced haptic feedback for a greater sense of touch in VR/MR (Harvard: Haptic interfaces source)
- Rumored Samsung XR headset joining the spatial computing race (The Verge: Samsung XR source)
- Improved passthrough video making MR more seamless
- Brain-computer interfaces for direct neural control
- 5G and edge computing enabling cloud-based XR experiences
The key difference remains: AR adds to your world, VR replaces it, and MR blends the two.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion: Choosing Your Reality
The ‘best’ reality depends on your goal. For quick, real-world information, AR is king. For total escape and immersion, VR is unmatched. And for the most futuristic, interactive experience, MR is leading the way.
As these technologies evolve, they promise to change how we work, play, and connect. Whether you’re using ScreenApp’s AI meeting assistant to enhance your virtual meetings or exploring AI video tools for content creation, understanding these immersive technologies helps you choose the right tools for your needs.
The future of human-computer interaction is here, and it’s more immersive than ever.



